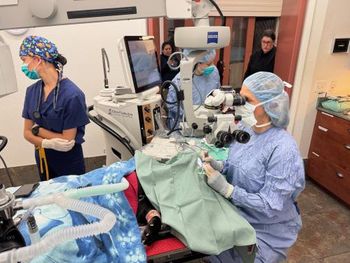
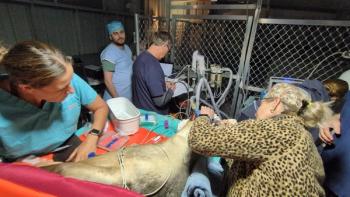
Alternative surgery for corneal endothelial dystrophy improves patients vision
Cyrus, a German shorthaired pointer, benefitted from the new procedure and provides hope for prevention of the disease.
Two times the luck. Cyrus benefitted from two separate clinical trials involving cornea disease at UC Davis, helping him to see better. (Photo courtesy of UC Davis.)
Life wasn't looking too bright last year for Cyrus, a 10-year-old German shorthaired pointer. Not only had he lost his home, he was also losing his sight. Living in a shelter, Cyrus was suffering from corneal endothelial dystrophy (CED), a disease that causes premature degeneration of endothelial cells, which are critical to pumping fluid out of the cornea and maintaining transparency.
CED is a devastating disease in dogs that can result in blindness and severe ocular pain from secondary complications. The endothelial cells make up the most inner aspect of the cornea and are responsible for maintaining a proper fluid balance. This function is critical to ensuring that the cornea remains transparent for vision. In many animals, including dogs, corneal endothelial cells have a limited capacity to regenerate after injury. In dogs with CED, the endothelial cells degenerate until the cells still remaining can no longer function properly. This results in swelling of the cornea, causing decreased vision, as well as formation of bullae on the cornea that can rupture and cause ocular discomfort.
There are palliative treatments such as hypertonic saline to decrease corneal bullae formation, but the only definitive treatment for this condition is corneal transplant (penetrating keratoplasty). Unfortunately, corneal transplants are rarely performed in dogs with CED because of the expense of the surgery and follow-up care, relatively high risk of complications and lack of appropriate donor tissue.
CED is seen more commonly in German shorthaired pointers than other breeds. Thus the disease may have a genetic component. Luckily for Cyrus and others of his breed, the UC Davis Veterinary Medical Teaching Hospital is conducting a clinical trial to identify the region of the dog genome associated with CED in German shorthaired pointers.
NorCal German Shorthaired Pointer Rescue in Menlo Park, California, found Cyrus, pulled him from the shelter, brought him to UC Davis and enrolled him in the trial. Researchers in the ongoing clinical trial, led by Sara Thomasy, DVM, PhD, hope that once the CED-causing gene is identified and isolated, they will be able to create a genetic test to allow breeders to avoid producing dogs with CED.
While Cyrus was helping UC Davis learn more about CED, Thomasy was considering whether a prior clinical trial on an alternative surgery to treat CED might hold promise for Cyrus.
“Based on the results of Cyrus' CED study, I was worried that he may not be a good candidate for the surgery,” said Thomasy. “His corneas were the thickest of any dogs on which this surgery had been performed.”
The prior surgery trial-conducted in conjunction with Animal Eye Center in Rocklin, California-was performed to discover the efficacy of an alternative to corneal transplant surgery. The alternative surgery involves performing a superficial keratectomy and then placing a thin conjunctival advancement flap over the removed portion. Known as a SKCAHF (superficial keratectomy and conjunctival advancement hood flap) surgery, the procedure thins the cornea in the region where the surgery is performed and, interestingly enough (for reasons unknown to researchers at this point), also in the central region that is left untouched. The alternative surgery trial showed promising results in nine enrolled patients, one of which was a German shorthaired pointer.
Based on the success of the SKCAHF surgery trial, Thomasy thought it would work on Cyrus, even though his corneas were so thick. Cyrus underwent a successful SKCAHF surgery in March 2014. Three months after surgery, he had markedly improved corneal clarity and vision.
“We did know that the SKCAHF surgery trial had been very successful in other dogs, including another German shorthaired pointer, but that dog had more moderate disease,” said Thomasy. “Cyrus' results are exciting because we now know this surgery can help dogs with severe disease, too.”
Cyrus' corneas are now less thick and clearer. His vision has dramatically improved, and he has been adopted.
UC Davis is still actively recruiting new candidates to find the genetic cause for CED in several dog breeds. If you have a German shorthaired pointer, German wirehaired pointer or a Boston terrier with CED, please contact Thomasy via email (smthomasy@ucdavis.edu) or phone (530-752-1770).
Newsletter
From exam room tips to practice management insights, get trusted veterinary news delivered straight to your inbox—subscribe to dvm360.