Stephen P. DiBartola, DVM, DACVIM
Articles by Stephen P. DiBartola, DVM, DACVIM

The volume and tonicity of body fluids are maintained within a narrow normal range by regulation of sodium and water balance. The volume of extracellular fluid (ECF) is determined by the total body sodium content, whereas the osmolality and sodium concentration of ECF are determined by water balance.
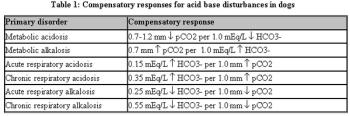
A proper understanding of the terms acidosis, alkalosis, acidemia, and alkalemia is necessary to differentiate simple from mixed acid base disorders. Acidosis and alkalosis refer to the pathophysiologic processes that cause net accumulation of acid or alkali in the body, whereas acidemia and alkalemia refer specifically to the pH of extracellular fluid. In acidemia, the extracellular fluid pH is less than normal and the [H+] is higher than normal.

Polycystic kidney disease was first described in adult male and female long-haired, Persian-type cats in the late 1960's. In 1996, the disorder was shown to be inherited as an autosomal dominant trait in a family of Persian cats. Both male and female cats were affected. In affected ? unaffected crosses, 42% of offspring were affected and 58% were unaffected. In affected ? affected crosses, 73% of progeny were affected and 27% were unaffected.

Despite recent technological advances in dialysis and transplantation, conservative medical management remains the most practical and accessible approach to the treatment of chronic renal failure (CRF) for most cat owners and veterinarians.

Fluid therapy is supportive. The underlying disease process that caused the fluid, electrolyte, and acid-base disturbances must be diagnosed and treated appropriately.

Over 90% of the potassium in the body is located within cells. External balance for potassium is maintained by matching output to input. Internal balance is maintained by translocation of potassium between intracellular and extracellular fluid. Any change in plasma potassium concentration must arise from a change in intake, distribution, or excretion.

A proper understanding of the terms acidosis, alkalosis, acidemia, and alkalemia is necessary to differentiate simple from mixed acid base disorders. Acidosis and alkalosis refer to the pathophysiologic processes that cause net accumulation of acid or alkali in the body, whereas acidemia and alkalemia refer specifically to the pH of extracellular fluid.

Despite recent technological advances in dialysis and transplantation, conservative medical management remains the most practical and accessible approach to the treatment of chronic renal failure (CRF) for most cat owners and veterinarians.

Fluid therapy is supportive. The underlying disease process that caused the fluid, electrolyte, and acid-base disturbances must be diagnosed and treated appropriately.

Polycystic kidney disease was first described in adult male and female long-haired, Persian-type cats in the late 1960's. In 1996, the disorder was shown to be inherited as an autosomal dominant trait in a family of Persian cats. Both male and female cats were affected.

Over 90% of the potassium in the body is located within cells. External balance for potassium is maintained by matching output to input.

The volume and tonicity of body fluids are maintained within a narrow normal range by regulation of sodium and water balance. The volume of extracellular fluid (ECF) is determined by the total body sodium content, whereas the osmolality and sodium concentration of ECF are determined by water balance.

Fluid therapy is supportive. The underlying disease process that caused the fluid, electrolyte, and acid-base disturbances must be diagnosed and treated appropriately.


