
Liver disease patients can present with a diverse clinical spectrum. Patients with mild liver disease can be expected to have fewer problems with general anesthesia than patients with severe, fulminant disease.

Liver disease patients can present with a diverse clinical spectrum. Patients with mild liver disease can be expected to have fewer problems with general anesthesia than patients with severe, fulminant disease.

Hypotension is a very common complication in the anesthetized patient, especially when the patient is maintained with inhalant anesthetics. Blood pressure is simple to measure in the anesthetized patient, and is very helpful to monitor depth of anesthesia and overall patient welfare.

Many types of anesthetic machines are now available for veterinary use. Retired machines from human hospitals are also commonly used by veterinarians.

Some random thoughts about cats: We all know they are not small dogs, but I think a certain discomfort with feline anesthesia persists with many veterinarians. Why is that?

Alpha-2 agonists have achieved widespread popularity in veterinary medicine for their sedative and analgesic properties. They can be valuable adjuncts in anesthetic protocols.

Many patients undergoing this diagnostic procedure will have signs of obstructive upper airway disease. They are dyspneic and easily stressed.

Multimodal analgesia, so called balanced analgesia, was introduced by Dahl et al in 1990 in order to minimize the adverse effects of opioids. These include respiratory depression, sedation, dysphoria,

General and specialty practice provide a number of analgesia challenges: those cases that dont fit the simple mold of opioids and NSAIDs.

The Cartesian model of pain imagines the somatosensory system as a simple, predictable, proportional line of communication directly linking, without altering, pain signals as they are transmitted from the periphery to the brain for conscious perception.

It is apparent that the primary, if not only, reason to assess pain is to take action to relieve pain. However, one of the most challenging responsibilities of veterinary professionals is pain assessment.

Whenever confronted with a painful animal, one should consider employing a considerable effort to control the pain as best as possible and as early as possible. T

Benefits of pain management in the acute situation

Acupuncture is the act of placing a needle into the body at a specific point in order to get a desired effect.

You can never become good at pain management without understanding basic pain pathways.

Probably the most common condition associated with osteoarthritis, post-surgery and musculoskeletal abnormalities.

Most commonly used veterinary pain drug

Small animal patients with cardiac disease and/or congenital abnormalities can be challenging and sometimes intimidating patients.

Seattle company to market medical marijuana patch to control pain in dogs, horses.

To make your pain control measures top-notch, construct a scaffold of appropriate pain medications.
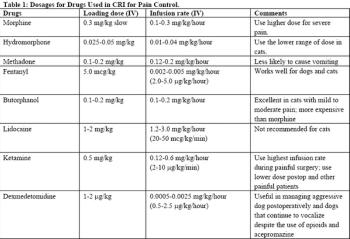
Constant rate infusion (CRI) analgesia is a way of providing pain control by ensuring that the blood levels of the drugs are held constant. In practice, it entails maintaining a venous access. This technique can be used during anesthesia as part of balancing the anesthetic technique and continued to the postoperative period.

Whether you are faced with anesthetizing a patient with the potential of increased intracranial pressure (ICP) or a patient with a spinal cord injury, there are special anesthetic considerations that should be made. Each patient should be thoroughly evaluated and an appropriate anesthetic protocol should be formulated.

In the veterinary profession, ?-2 adrenergic receptor agonists (?-2 agonists) are either loved or feared; this is often determined by a veterinarian's familiarity with the drug. There is no doubt that ?-2 agonists have complex effects, but understanding ?-2 agonists increase options for analgesic use, as well as sedation.

Used in veterinary medicine mostly for acute pain. Oral opioids have poor absorption in animals so there is a tendency not to use them in chronic conditions. All opioids have peripheral and central effects.

Local anesthesia is employed prior to all dental procedures. Dental procedures can be very painful. The patient often can feel dental procedures while under inhalation anesthesia.

Synthetic opioids are powerful, useful tools to manage pain for one simple reason: Receptors for naturally-occurring opioids (endorphins, enkephalins) are distributed ubiquitously throughout the body and can be found in both central and peripheral tissues.