
Foaling, like human delivery, should be uneventful. But the process can be fast and violent, and it can present serious health problems to the mare and foal.

Foaling, like human delivery, should be uneventful. But the process can be fast and violent, and it can present serious health problems to the mare and foal.
The American Heartworm Society's symposium addresses newest threats.

Duluth, Ga. -- Merial and the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) have worked out a new system to ease the shortage of its heartworm treatment Immiticide, the company reports.

Boston -- Devocalizing a dog or cat without medical cause will be a felony in Massachusetts if Gov. Deval Patrick signs a newly presented bill into law.

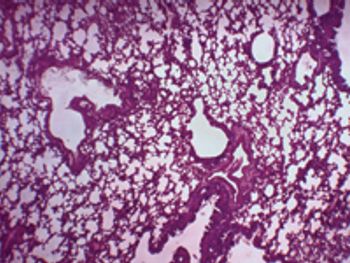
Close attention to detail in evaluation of history and clinical findings, accurate and appropriate sample collection, maintenance of chain of custody of evidence and judicious use of analytical testing are imperative when investigating suspected intentional animal poisonings.

Soft tissue injuries and osteoarthritis are common conditions afflicting active dogs due to the repetitive forces placed on the joints. Microtrauma to the tendons, ligaments, and the articular surfaces of joints can occur, creating an environment for osteoarthritic development.

Each year in the United States millions of homeless or unwanted dogs and cats are euthanized in animal shelters and humane societies. While precise numbers are difficult to obtain the estimates range from 3 to 4 million.

The etiology of chylothorax is often not identified. Although trauma is listed as a potential cause in some sources, there is no evidence that it would be responsible for persistent chylothorax.

Injuries to the carpus and tarsus are common in agility and sporting dogs. The carpal and tarsal joints act as sock absorbers for the limb during weight bearing.

Baits may come in the form of gels injected with a preloaded syringe or incorporated into a plastic housing. The bait may be mixed with food stuffs such as peanut butter, jelly, and bread crumbs to attract the insects. Most of the insecticides used in these products are of low mammalian toxicity; exposure to these insecticides cause little more than gagging or vomiting.

For the committed dog breeder, what begins with a single pet as a casual hobby evolves into an avocation that is truly life-transforming. Often their every minute and dollar are expended in pursuit of their chosen "dog sport:"

A common and often frustrating problem encountered in small animal medicine is chronic vomiting. Chronic gastrointestinal disease in young animals is often caused by parasitism, dietary indiscretion, congenital disease (megaesophagus), and breed-associated diseases, whereas disease in the older animal is often a result of neoplastic and infiltrative disease.

Aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid, ASA) is available as tablets, capsules, powders, effervescent tablets and oral liquid preparations. Aspirin reduces pain and inflammation by reducing prostaglandin and thromboxane synthesis through inhibition of cyclooxygenase. At very high dosages, aspirin and other salicylates uncouple oxidative phosphorylation, leading to decreased ATP production.

Internet rumors are probably the most modern form of folklore (handed-down beliefs, stories, and customs), following on the heels of faxlore, xeroxlore, chain letters, and campfire stories.

Diagnosing and treating forelimb conditions in dogs can be very challenging. Many dogs present with a similar history including minimal responsive to rest and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and increased lameness following exercise and heavy activity.

Dogs that present with the vague client complaint of "ain't doin' right" can be a particularly difficult diagnostic challenge when the only significant finding on a routine physical examination is fever. The cryptic fever becomes even more challenging when the results of routine diagnostic laboratory work fail to localize the disease process.

The most common hind limb orthopedic/sports medicine conditions afflicting active dogs are iliopsoas strains, cranial cruciate ligament (CCL) insuffiency and gracilis and semitendinosus contracture.

There is a homeless pet crisis in the United State that is a direct result of animals left unaltered in our communities. ASPCA and HSUS estimates are that 6-8 million animals are placed in shelters each year and of these 3 – 4 are euthanized. That equates to one animal euthanized every 2 seconds every working day each year.

Veterinarians that care for service dogs such as police, military, and search and rescue dogs are entrusted in maintaining the health of animals that provide a vital service to man, especially during times of crisis such as the terrorist events of 2001, when the searching abilities of the these dogs were of paramount importance.

Antidotes can be divided into three broad catagories: chemical antidotes, pharmacologic antidotes, and functional antidotes. Chemical antidotes act directly on the toxicant to make it less toxic and/or more readily excreted. Pharmacologic antidotes antagonize toxic agents at their receptor sites or through other macromolecules.

The objective of this session is to provide the practitioner with the knowledge required to effectively manage a canine breeding.
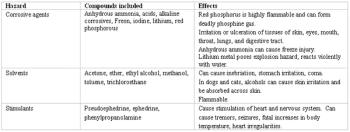
Methamphetamine, also known as Meth, Speed, Ice, Crystal, Chalk, Crank, Tweak, Uppers, Black Beauties, Glass, Bikers Coffee, Methlies Quick, Poor Man"s Cocaine, Chicken Feed, Shabu, Crystal Meth, Stove Top, Trash, Go-Fast, Yaba and Yellow Bam, is a highly addictive and powerful stimulant drug.

Think back to when you first learned to perform ovariohysterectomies and neuters. It is probable that you were taught these procedures early in your surgical education at a time when you had limited surgical skills.

In the field of small animal orthopedics, orthoses, prostheses and other assistive devices are an emerging technology that can aid in the well-being of our canine patients. These devices are used to either correct or accommodate the affected limb(s) following trauma or surgical intervention, and may be utilized as temporary or permanent modalities.

The normal male dog attains puberty at approximately 6 – 8 months of age. Sexual maturity is generally attained at 18 – 30 months. Males may successfully breed bitches prior to sexual maturity but they will not achieve maximal fertility or daily sperm output until mature.
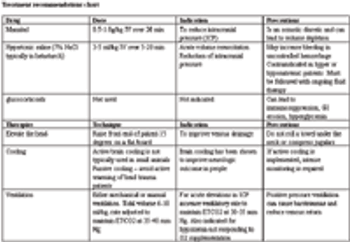
Head trauma can result from a variety of different types of injury in dogs and cats. The aim of treatment for head trauma is the prevention of secondary brain injury.
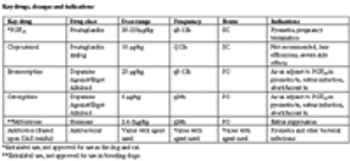
When pyometra occurs in a pet animal, the decision for surgical intervention is uncomplicated. When pyometra occurs in a valuable animal intended for breeding, the breeder client often opts for medical treatment.

Canine breeding management centers hinges on ovulation timing. Ovulation timing is important because it is critical to have viable spermatozoa in the bitch's oviducts at the time the eggs are mature and ready to be fertilized.

A new study links premature human and animal deaths in poor neighborhoods.

Are synthetic surfaces leading to a decline in fatal injuries in races?