
The Zoological Education Network introduces A Practitioners' Guide to Avian Necropsy.

IDEXX Laboratories, Inc. announces the availability of its LaserCyte? Hematology Analyzer, the next generation in veterinary hematology testing for equine veterinarians.

IDEXX Laboratories, Inc. received approval from the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) to produce and sell the IDEXX HerdChek? BSE Antigen Test Kit to USDA-approved laboratories.

Fort Dodge Animal Health received approval of Duramune Adult, the first USDA-licensed vaccine with three-year virus challenge data against a trio of deadly canine diseases; canine parvo (CPV), canine distemper (CDV) and canine adenovirus (CAV). The new vaccine will be available in the second quarter of 2004.

Goldway U.S. introduces its new patient monitors for animal surgery, diagnostics and research.

The University of Georgia's Glass Horse Project introduces a new CD entitled Elements of the Equine Distal Limb.

Cleveland- Legislation and lawsuits surfacing in the United States reveal a dithering balance between the profession's defense of veterinary medicine and the public's desire to increase pet value via legal status, classification and economic worth.

Kitty's WonderBox, manufacturer of the disposable, biodegradable cat litter box of the same name, introduces All in Wonder Post-Op a disposable litter box and cat litter in one package designed for use by veterinarians.

Merial rounds out its rabies vaccine line with the launch of IMRAB?1 TF, a one-year, thimerosal-free (TF) vaccine for dogs and cats.

Securos Veterinary Orthopedics offers a high-quality pin cutter with removable handles.

Portland, Ore.-Banfield, The Pet Hospital has reached an agreement with Fort Dodge Animal Health to conduct a clinical field trial on newly approved canine Duramune Adult vaccine with three-year duration of immunity data for distemper, hepatitis and parvovirus (DHP).

Dairies now have the ability to locate quality dairy heifer growers via the Internet.

Tampa, Fla.-According to Dr. Robin Downing, of the Windsor Veterinary Clinic, Windsor, Colo., compliance is a quality of care and a quality of life issue. When viewed in this context, being an advocate for a pet that cannot advocate for itself is a "no brainer."

Pedigree Perfection introduces novelty fashion with its scrub shirts for dogs.

Securos Veterinary Orthopedics offers a meniscus grabbing forceps that is ideal for dealing with the meniscus during cruciate repair surgery.

Synbiotics announces the launch of its newly revised and updated Web site at www.synbiotics.com.

Sand-Gard, produced by Natural Animal Feeds ? USA, is used as a preventive measure against sand colic and helps to maintain a healthy gut environment, the company says.

Lonza Inc. introduces L-Carnipure? products containing L-Carnitine, an amino acid derivative believed to support healthy cardiac and hepatic functions as well as aid fat metabolism, the company says.

All-Pro Imaging has introduced a quartet of CR scanners to the veterinary market that are suitably sized and priced for the private office.

Wysong Corp.'s line of companion animal products now includes the tooth powder treat Dentatreat.

Whether adding staff or services, veterinary hospitals commonly have a hard time accepting change.

We built a rack for our endotracheal tubes that allows the tubes to hang like stemware from a wine glass rack.

I use a flea comb to hunt down stray sutures buried in hair or crusts.

To weigh cats and small dogs, we use a digital package scale.
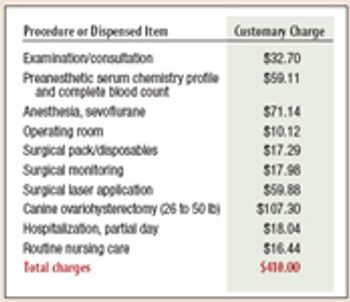
When quoting fees for ovariohysterectomies, we use a prepared itemized fee quote showing the regular charges for each service.

An extensive amount of hair can remain in the wound after shaving, wiping, and flushing.

St. Paul, Minn.-The University of Minnesota's (UM) College of Veterinary Medicine has unveiled an endeavor to recruit students with food animal interest earlier in their academic career.

Accountability is responsibility taken to the next level.

There's a hidden "occupational hazard" new graduates aren't likely to find in any OSHA manual, according to one expert.

Increasingly vulnerable to lawsuits and state board complaints, veterinarians remain on the lookout for liability concerns in their practices, and graduates should beware of the pitfalls of not working in a legally sound environment.