CAPC predicts higher heartworm risk, continued spread of Lyme disease in 2019
Southeast, Atlantic Coast and Midwest are of particular concern for veterinary parasites this year.
The Companion Animal Parasite Council (CAPC) this week released its annual 2019 parasite forecast and corresponding 30-day forecast maps to alert veterinarians and pet owners of pending outbreaks. The organization predicts that heartworm will be higher than average, especially in the Southeast United States; the forecast for Lyme disease is for a continued spread in the Atlantic Coast and Midwest.
“We started providing our annual forecasts over eight years ago because of the dynamic and ever-changing nature of parasites,” says Christopher Carpenter, DVM, executive director of CAPC, in a release from the organization. “Over the years, we have seen these diseases continue to move. Our annual forecast will alert pet owners to the risks this year and remind them that our pets need to be tested and protected year-round.”
Pet owners and veterinarians who want to monitor parasite activity in their county throughout the year now have access to 30-Day Parasite Forecast Maps at petdiseasealerts.org. These maps provide a local forecast for every county in the continental United States on a monthly basis. In addition, the parasite prevalence maps at capcvet.org provide a snapshot of the percentage of pets that have tested positive for a given disease, also down to the county level.
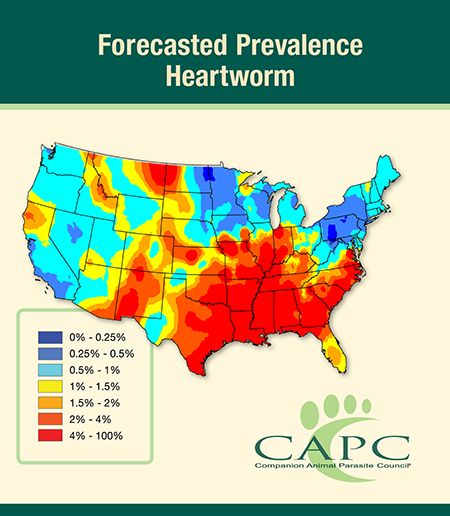
According to CAPC, the risk of pets acquiring heartworm disease is increasing due to weather patterns and the transportation of companion animals from one area of the country to another. A warmer-than-usual and humid weather pattern has created an ideal breeding condition for mosquitoes across the country, which increases potential transmission of the parasite that causes heartworm disease.
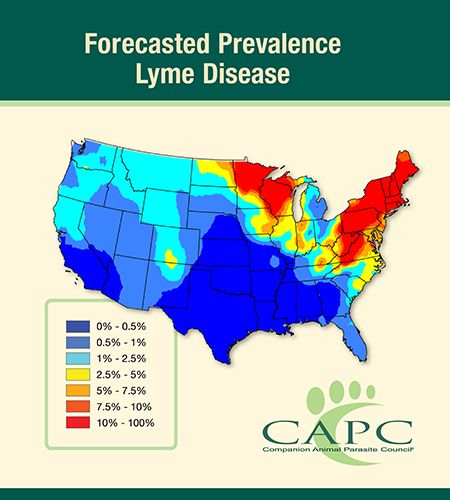
CAPC also predicts that Lyme disease will be higher in three key areas this year: the Appalachian region, Minnesota and the Atlantic Coast. Lyme disease, which is transmitted by Ixodes species ticks, is spreading as the white-tailed deer population grows and migratory birds carry ticks to new areas. The organization urges veterinarians and pet owners to test annually and use tick preventive/acaricidal treatment year-round. High-risk patients for vector-borne disease should be tested and their owners should consider a vaccination for Lyme disease, CAPC says.
Here are more specifics on CAPC's risk predictions regarding parasite-related diseases:
Heartworm infection is expected to be higher than average in the south-central and southeastern United States. The areas of greatest concern are those along the Mississippi River from northern Louisiana all the way into Illinois.
In addition, areas with historically lower prevalences of heartworm should particularly take note of predicted higher prevalence including Indiana, Illinois and Iowa, CAPC says. Southern Louisiana and a small area along the Texas border are currently forecasted to be lower than average. Pet owners should take extra care to limit their pets' exposure to mosquitoes, test their pets annually for heartworm diseases and use heartworm preventatives year-round.
Lyme disease is a high threat again this year and is “oozing” into the entire Appalachian region, the Atlantic Coast, and throughout Wisconsin and Minnesota, CAPC says. Pets living in or traveling to these states are considered to be at high risk; pet owners are adivsed to talk to their veterinarian about a Lyme vaccination in addition to testing for the disease and protecting year-round against ticks.
Transmission of the agents of anaplasmosis is forecasted to be average for much of the United States. However, northwestern Minnesota could have a more active year. Some other spots are expected to see less activity than normal, including the Atlantic Coast of New England, the Wisconsin-Minnesota border, the Upper Peninsula of Michigan and southern Texas.
Ehrlichiosis is expected to be higher throughout the south-central United States, particularly in Oklahoma, Arkansas and Missouri. There are several small areas scattered throughout the south-central and southeastern states that are predicted to be lower than average, most notably eastern Arkansas and across the border of North Carolina and Virginia.
The CAPC Parasite Forecasts are a collaborative effort among parasitologists and statisticians in academic institutions across the United States, the organization states. These researchers conduct research and analyze data that helps them understand and monitor the transmission of vector-borne disease agents and the changing life cycles of parasites. The forecasts are based on many factors, including temperature, precipitation and population density.
