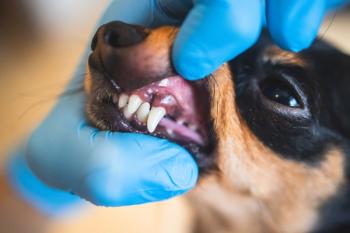
Periodontal disease: Therapies and home care strategies (Proceedings)
Defined as an inflammation and infection of the tissues surrounding the tooth, collectively called the periodontium.
Understanding periodontal disease
- Defined as an inflammation and infection of the tissues surrounding the tooth, collectively called the periodontium.
- Systemic affects from bacteria present can compromise liver, kidneys and heart.
- Returning the mouth to a healthier state with a thorough cleaning and periodontal therapy affects the overall health of the patient.
Etiological timeline
- A glycoprotein component of saliva (acquired pellicle) attaches to the tooth surface.
- The pellicle takes only 20 minutes to form and helps bacteria attach to the tooth surface.
- About 6-8 hours after pellicle formation, bacteria start to colonize the tooth surface-this is what we know as plaque.
- The bacteria that have colonized the surface die. The bacteria that are attached to the tooth absorb calcium from saliva and become calcified-what we know as tartar or calculus.
More fun facts
- The bacteria present in the normal oral flora consist primarily of gram-positive aerobic bacteria.
- As periodontal disease progresses, gram-negative bacteria begin to colonize the tooth surface. Specifically, black-pigmented anaerobic bacteria (BPAB).
- The bacteria are arranged in what is called the biofilm-it is the disruption of this biofilm, more than anything else that is important in the control of periodontal disease.
- Patient Response
- As the bacteria infiltrate and colonize the pocket between the free gingiva and tooth, known as the sulcus, the patient attempts to fight the infection.
- White blood cells are sent in to attack the bacteria.
- The bacteria often contain endotoxins and enzymes that are toxic to gingival tissues, specifically collagenase, an enzyme which breaks down tissue.
- Gingivitis, loss of tissue (gum recession), furcation exposure, bone loss, and eventually tooth loss can occur without treatment.
Staging periodontal disease
- The worst tooth is used to establish the stage of periodontal disease.
- Periodontal staging is based on factors such as plaque, calculus, inflammation and topography. Can be done in the awake patient if cooperative
- The anesthetized patient should have each tooth evaluated and charted for effective treatment.
- Healthy Gingiva (Stage 0) has a knifelike margin, smooth topography (the surface features of the gingiva as if flows from tooth to tooth), and normal sulcus depth 2-3 mm in dogs, 0.5-1 mm in cats.
- Early Gingivitis (Stage 1) is limited to gingival tissue and appears reddened, with a mild amount of plaque.
- This is the only stage that is reversible.
- Early Periodontitis (Stage 3) There is a moderate loss of attachment and moderate pocket formation.
- There is also some degree of furcation exposure (the space between tooth roots where the roots join the crown). There is also a fair amount of gingival bleeding when probed.
- Established Periodontitis (Stage 4) A significant amount of bone loss and attachment structures is noted with severe pocket depths. Significant gum recession and tooth mobility are also present. These patients usually have a strong odor, and pus may be present in the oral cavity
Management of PD begins with prevention
- Client education regarding local and systemic effects can help with client compliance.
- Home care for every patient-give owners options to help with client compliance. Home care options can include dentifrices, CET chews, dental diets, plaque prevention gel, etc.
- The goal of periodontal therapy is to keep the teeth as clean as possible, thereby reducing the number of pathogenic bacteria that destroy periodontal tissues.
The four main objectives of periodontal therapy include removing the biofilm (plaque, tartar), minimizing attachment loss, minimizing pocket depth, and maintaining a minimum of attached gingiva.
Advanced periodontal therapies
The following can and should be performed in general practice to treat most periodontal disease.These therapies can be performed by a technician with the correct training. Charging appropriately for treatment of periodontal disease can significantly increase revenue in the practice.
Ultrasonic Periodontal Debridement removes calculus and debris subgingivally. It also disrupts the cell wall of bacteria thereby destroying it. This procedure is performed with a specific ultrasonic periodontal tip which can be used safely subgingivally.
Subgingival Curettage is the debridement of the periodontal pocket to encourage healing and reattachment of gingiva to reduce pocket depth. This technique is performed with a curette.
Closed root planing is the debridement of the root, to remove a layer of cementum, soft and hard substrate, and diseased sulcal lining. The purpose of root planing is to remove irregularities and a thin layer of superficial cementum-loaded with bacterial toxins-that will inhibit healing if left in place._ The instrument used is also a curette with the Modified Pen Grasp technique.
Perioceutic placement-doxirobe gel
Placement of doxycycline gel is used in periodontal pockets of 4 mm or greater. This acts as a barrier to prevent epithelial tissues from reinhabiting the pocket and allowing the periodontal tissues to grow. It also provides antibacterial properties, immunoregulatory properties to dampen the inflammatory response, and anti-collagenase properties which counteract the tissue destruction process.
More advanced periodontal therapies
The following therapies can be performed in general practice. They are considered oral surgery and should be performed by a veterinarian with advanced training. Always recommend referral to a dental specialist if treatment needed is beyond your capabilities. Gingival Flaps with open root planing are performed on periodontal pockets 6mm or greater. By creating a gingival flap, it allows for better visualization into the deeper pockets for more effective removal of tartar, bacteria laden cementum and debris. A 12% EDTA solution is then placed to dissolve debris and open the dentinal tubules. A bone graft material is then placed to promote bone growth around the affected tooth.
Raising the bar
Periodontal therapy techniques improve the dental care of your patients. These therapies allow the practitioner to treat and save teeth as opposed to premature extraction. These techniques are important to master not only for the improved health of the patient, but also to increase revenue for the practice.
References
1 S.E. Holmstrom Veterinary Dentistry for the Technician & Office Staff (Saunders 2000) pg. 149_2 S.E. Holmstrom Veterinary Dentistry for the Technician & Office Staff (Saunders 2000) pg. 149_3 S.E. Holmstrom Veterinary Dentistry for the Technician & Office Staff (Saunders 2000) pg. 150_4 H. Lopbrise, R. Wiggs Common Dental Procedures (AAHA Press 2000) pg. 47_5 S.E. Holmstrom, P. Frost, E. Eisner Veterinary Dental Techniques (Saunders 2004) pg. 240_6 S.E. Holmstrom, P. Frost, E. Eisner Veterinary Dental Techniques (Saunders 2004) pg. 237_
Newsletter
From exam room tips to practice management insights, get trusted veterinary news delivered straight to your inbox—subscribe to dvm360.