Radiography vs. ultrasonography-which one to use to make the diagnosis (Proceedings)
A review of the indications for radiography and ultrasonography.
Indications for Radiographic Examination
• Overview
• Size, shape, position, contour, opacity
• Very good for bone and gas-skeletal system, lungs
• Contrast studies-GI series, IVU, cystourethrogram, vaginogram enhance ability to define structures.
• Can only see four opacities-gas, fat, bone and "soft tissues"
• Need one opacity surrounding something of a different opacity to be able to define it radiographically
Indications for Ultrasound Examination
• Individual soft tissue organ composition
• Dynamic blood flow
• Not so good for bone and gas

Abdominal Cavity
a. Method Of Choice For Detecting Etiology For Peritoneal Fluid.
1. Fluid Acts As "Acoustic Window/Contrast Medium" Which Help Visualization Of Intra-Abdominal Structures.
2. Abdominal Masses Can Be Assessed Despite The Presence Of Hemorrhage.
b. Liver Can Be Evaluated, Espeically Its Architecture And
c. Contour.
1. Focal Lesions-Metastasis, Nodular Hyperplasia.
2. Mass Lesions-Abscess, Cysts, Neoplasia
3. Hepatic Congestion
4. Vascular Abnormalities-Shunts, Av Fistula
5. Cirrhosis
d. Hepatobiliary System-Indicated In Presence Of Jaundice
1. Cholelithiasis
2. Extra-Hepatic Biliary Obstruction, Enlarged Common Bile Duct
3. Enlargement Of Intrahepatic Bile Ducts
4. Neoplasia Involving Biliary System
5. Obstruction Due To Pancreatic Disease
e. Spleen-Indicated In Presence Of Splenomegaly And Blood Dyscrasias
1. Torsion
2. Neoplasia
3. Nodular Hyperplasia
4. Infection
5. Infarction
6. Hematoma
f. Urogenital System
1. Pregnancy Diagnosis 10-25 Days Post-Breeding
2. Fetal Viability
3. Ovarian Masses, Cysts
4. Infertility
5. Pyometra/Hematometra
6. Ovarian Pedicle And Uterine Stump Pyogranuloma
7. Scrotal Enlargement-Neoplasia, Hydrocele
8. Location Of Retained Testicle
9. Prostate Gland-Hyperplasia, Cysts, Abscesses, Neoplasia
10. Kidneys-Neoplasia, Cysts, Abscesses, Hydroureteronephrosis, Glomerulonephrosis/ Nephritis, Mineral Deposition/Calculi, Toxicosis, Fibrosis, Hypoplasia/Dysplasia
11. Urinary Bladder-Neoplasia, Infection, Neoplasia, Wall Thickness
g. Other
1. Pancreas-Neoplasia, Pancreatitis
2. Adrenal Glands-Hyperplasia, Neoplasia
3. Gastrointestinal Tract-Neoplasia, Intussusception, Infiltrative Diseases
4. Lymph Nodes-Mesenteric, Retroperitonel Enlargement
5. Peritoneum-Carcinomatosis, Mesenteric Masses
6. Retroperitoneum-Effusion, Hemorrhage, Lymph Node Enlargement
7. Hernia-Diaphragmatic, Pericardial-Peritoneal, Body Wall
8. General Abdominal Survey
Thoracic Cavity
a. Method Of Choice When Pleural Fluid Is Present
b. Heart
1. Cardiomyopathies – Dilated, Hypertrophic
2. Acquired Diseases – Mitral Insufficiency, Endocardiosis, Endocarditis
3. Neoplasia-Heart Base, Right Atrial
4. Thrombus
5. Congenital Diseases – Pda, Septal Defects, Pulmonic And Arotic Stenosis, Valve Dysplasia
6. Evaluate Response To Therapy
c. Pericardial Disease-Masses, Fluid, Thickness
d. Mediastinum-Neoplasia, Abscesses
e. Lymph Nodes
f. Lung Masses When Adjacent To Thoracic Wall Or Diaphragm
g. Pleural Masses
h. Heartworm Disease

Comparison â Ultrasonic Image To Radiographic Image
Miscellaneous
a. Ocular
1. Evaluate Internal Ocular Structures In Presence Of Hemorrhage Or Corneal Scarring
2. Retinal Detachment
3. Lens Luxation
4. Intra-Ocular Neoplasia Or Foreign Body
5. Retrobulbar Area – Neoplasia, Abscess, Foreign Body
b. Vascular Structures—Enlargements, Thrombosis, Catheter Localizations, Neoplasia
c. Any Soft Tissue Body Surface Mass – Determine Size Architecture, Invasiveness, Vascularity
d. Retropharyngeal Masses-Neopalsia Thyroid, Lymphadenopathy, Abscesses
Organ Systems And Disease are Defined By Their:
Echogenicity – The Echogenic Composition Of The Tissue And Its Composition Compared To Other Tissues.
• Size
• Shape
• Location
• Contour
• Blood Supply
• Motion
• Distortion Of Adjacent Tissues
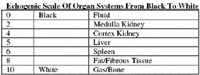
Echogenic Scale Of Organ Systems From Black To White
Diagnostic Ultrasound: Key Terms
Echogenicity – Refers To The Amount Of Sound Returned To The Transducer From An Object And/Or Interface
• Low Echogenicity –Minimal Amount Of Sound Returned
• High Echogenicity –Maximum Amount Of Sound Returned
Anechoic Without Sound
Hypoechoic Lesser Amount Of Sound
Isoechoic Similar Amount Of Sound
Hyperechoic Greater Amount Of Sound
For Routine B Mode Ultrasound, The Convention Used Is To Have The Screen Black And Any Sound Detected Is Displayed
As A White Dot; Using This Convention.
Anechoic – Meaning Without Sound – Is Displayed As BLACK
Hyperechoic – Meaning With A Greater Amount Of Sound – Is Displayed As WHITE
Isoechoic – Meaning A Similar Amount Of Sound – Is Displayed As The SAME COLOR
Hypoechoic – Meaning With A Lesser Amount Of Sound – Is Displayed As DARKER
Veterinary scene down under: Australia welcomes first mobile CT scanner, and more news
June 25th 2024Updates on the launch of the first mobile CT scanner available for Australian pets; and learn about the innovative device which simplifies placement of urinary catheters in female dogs
Read More