
Some diabetic dogs are insufficiently controlled with NPH insulin. Here's a look at a possible alternative.

Some diabetic dogs are insufficiently controlled with NPH insulin. Here's a look at a possible alternative.

New research shows sensitivity to trilostane may increase as body weight increases.

Advice on a geriatric cat with hyperthyroidism, renal disease, and diabetes.

A sodium:potassium ratio combined with white blood cell counts may hold the key to diagnosis.

Listen to the experts discuss nutritional management of hyperthroid cats.

Owning a diabetic cat gave this internist additional insights into how best to manage diabetic cats at home.

Dr. David Bruyette helps determine the best course of action.

Dr. David Bruyette tackles the case of a cat with two endocrine diseases.

A Q&A with Dr. Lori Wise reveals strategies for managing diabetic cats and dogs.
A 13-year-old 10.3-lb spayed female domestic shorthaired cat was presented to VCA West Los Angeles Animal Hospital for progressive and unresolving lethargy over the course of two to three days and one episode of vomiting.

Dr. Joseph Bisignano explains when you should add this disorder to your differential diagnosis list.
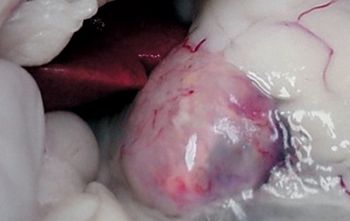
Now that you've diagnosed this disorder, it's time to decide whether to treat it medically or surgically.

Dr. Lori A. Wise answers questions about managing the rise in diabetes in companion animals.

The role of this hormone in diagnosing hyperthyroidism is an area of active research in veterinary medicine.

Dr. J. Catharine Scott-Moncrieff reveals the keys to insulin control.
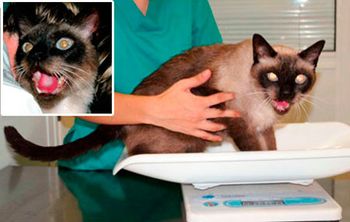
What's causing this cat's open-mouth breathing and frantic facial expression?

What is causing this dog's clinical signs?

Dr. David Bruyette helps a reader with a difficult endocrinology case.

Owners think the disease has a greater negative impact on their own lives than on those of their cats.

The goal of this study was to evaluate the effects of lower-dose trilostane treatment.

Diabetes Mellitus (DM) and hyperadrenocorticism (HAC) are common endocrinopathies in dogs that often occur simultaneously in the same patient. Diagnosis and management of concurrent disease may be a challenge to the practitioner since many clinical signs of DM and HAC are similar.

Pathogenesis: Insulin-dependent, non-insulin dependent, and transient

Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis--classic endocrine feedback loop

Thyrotoxicosis is a term used to describe any condition in which there is an excessive amount of circulating thyroid hormone whether from excess production and secretion from an overactive thyroid gland, leakage from a damaged thyroid gland, or from an exogenous source.

Ketone bodies: acetoacetate, beta hydroxybutyrate, acetone