
Mortality rates in the dairy industry are much higher than those in the cow calf or feedlot industries.

Mortality rates in the dairy industry are much higher than those in the cow calf or feedlot industries.

The examination should begin with a complete history in regard to the previous uses and the previous breeding experiences and outcomes if available.

Diagnosing and treating acute and chronic causes of vomiting and diarrhea.

Case 1: 5-year old Angus cow, calved 3 weeks ago
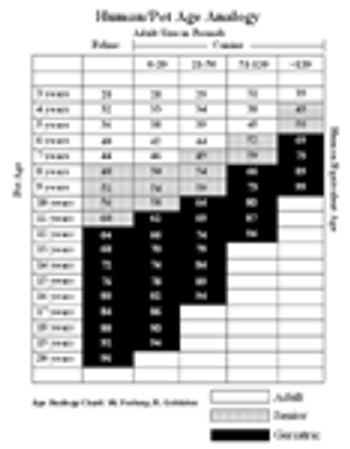
In the last AVMA pet owner survey, more than 39% of the owned pet population were 7 years of age or older and these percentages continue to grow.

Bovine viral diarrhea virus (BVDV) is one of the most important viral pathogens of cattle worldwide.

Canine and Feline liver disease diagnosis and treatment has improved dramatically over the last 20 years due to clinicians working to obtain a definitive diagnosis with improved diagnostic procedures.

It is known that high blood pressure is associated with renal disease in many species including cats and dogs.

Infectious conditions like respiratory diseases, reproductive diseases and neonatal diarrheas continue to "plague" animal owners.

Development of fertility diagnostics and therapeutics offers enhanced productivity and economic opportunity for the cattle industry through increased reproductive efficiency.

As a veterinarian working in the field, if you suspect that a foreign animal disease (FAD) is present, your obligation is to promptly report it to the appropriate authorities.

Lameness examination: Examined at a distance, then up close by hands-on.

While the leading causes of calf illness and death within the first few days after delivery are non-infectious physiological disturbances, after that time, the majority of illness and death losses are attributable to infectious conditions.

Bovine viral diarrhea virus (BVDV) has emerged as one of the most important infectious disease agents in cattle.
Immunoglobulins cannot traverse the placenta in cattle, so calves are born without any innate immune protection.

Vaccination is an important tool in veterinary medicine, preventing disease and reducing virus circulation for many important viral pathogens.

Forage test reports are like short stories.

Primary motility disorders of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract in the dog and cat are not well studied.

Dairy production systems in the US have changed considerably over the last several decades due to forces that promote economic efficiency of production and to scientific and technological advances that afford opportunities for change.

In the overwhelming majority of cases (except when a veterinarian delivers a calf in dystocia), the owner/herd manager will be the person best positioned to combat newborn calf health problems.

Many zoonotic diseases are bacterial in origin.

Bitches generally attain puberty two to three months after reaching adult body size.

Primary gastric neoplasia is an important differential diagnosis for a dog or cat with vomiting, especially chronic vomiting, anorexia and weight loss, particularly animals that are middle-aged and older.

Over the last several decades we have witnessed tremendous changes in dairy production systems.

An outbreak of respiratory disease occurred in a kennel of racing greyhounds in 2004.

Feline infectious peritonitis (FIP) continues to be a significant disease in domestic cats.
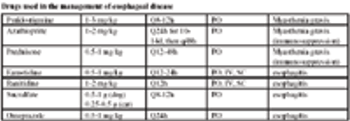
Esophageal disease can easily sneak up on the unsuspecting clinician if regurgitation, the cardinal sign of esophageal disease, is not considered a differential diagnosis for an animal that presents for what the owner perceives as vomiting.
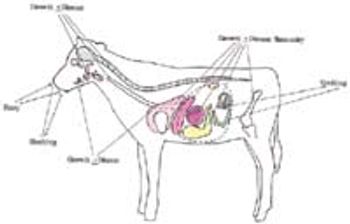
Direct transmission requires that animals be in close, intimate contact because the animal-free state of the virus must be very short in order to effect a successful transmission of viable virus.

When I report back to a cattle owner that his animal is "BVD positive," before I can even begin to explain what that means, I am all to often asked "what is BDD, BV . . . what?" since I am usually talking to the rancher about a normal calf , not an obviously sick animal.