
The neonatal development can be divide into specific time periods; the neonatal period (birth - 2 weeks); the transitional period (2-4 weeks); the socialization period (4 -12 weeks), and the juvenile period (12 weeks - puberty).

The neonatal development can be divide into specific time periods; the neonatal period (birth - 2 weeks); the transitional period (2-4 weeks); the socialization period (4 -12 weeks), and the juvenile period (12 weeks - puberty).

Approximately 20 years ago, studies centered on the ability of bull sperm to fertilize eggs in vitro.

The testis can be affected with several types of tumors.

Vaccine types, delivery methods and adjuvants in use in veterinary medicine have been relatively static for many years and limited to modified live organism and killed organism (KV) vaccines, needle injection and alum-type and water –in-oil emulsion adjuvants.

Indications for Karyotyping include possible testicular hypoplasia/aplasia, abnormal external phenotype (e.g. small penis, ambiguous genitalia), and suspected congenital lesions associated with infertility.
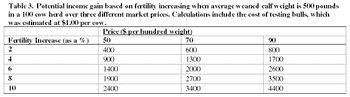
Fertility-associated antigen (FAA) is a non-glycosylated protein produced in all of the accessory sex glands of bulls; seminal vesicles, prostate and Cowper's glands.

Gastrointestinal (GI) cytology offers many advantages to the small animal practitioner in the assessment of patients with gastrointestinal tract disease.

Unlike bacterial infections, parasites are much easier to prevent.

An ulcer is defined as a loss of epithelium from the mucosal surface of the abomasum.

The Michigan Johne's Disease Control Demonstration Project is a cooperative program between Michigan State University (MSU), Michigan Department of Agriculture (MDA), and the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA).

The infertile animal is commonly presented with historic evidence of an unsuccessful breeding.

"Downer" animal: Animal with prolonged recumbency (>12 hrs) that is persistent and intractable

The male is prepared for semen collection by placing him in a quiet area with minimal disturbances.

Fractures of the metatarsal/metacarpal regions commonly occur in food animal practice particularly in young calves.
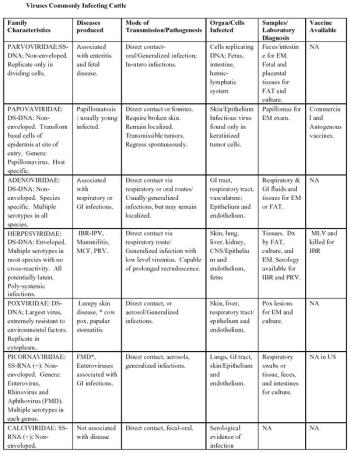
Animal viruses are now classified into 16 separate families.
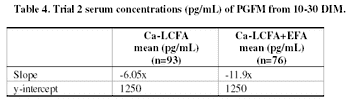
Supplying fat in dairy cattle rations has become a common practice on commercial dairies, as it is an effective way to supply energy to the cow.
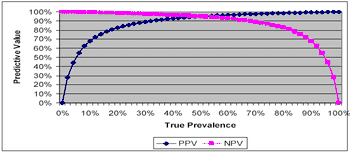
The innate sensitivity and specificity of a diagnostic test affects its validity, i.e. how well a test reflects the true disease status of an animal.

Bovine leukemia virus (BLV) is an oncogenic retrovirus associated with lymphosarcoma in cattle.

While scores of potentially toxic plants may be ingested, relatively few plants account for the majority of exposures.

Definition/Etiology: Infectious, transmissible disease of cattle, sheep and goats. Caused by the Rickettsial organism Anaplasma marginale in cattle or A. ovis in sheep/goats.

Bovine viral diarrhea virus (BVDV) is one of the most important infectious agents of cattle.

The cause of IMHA has been discussed at length.

The disease is a result of immune complexes accumulating within the glomerulus.
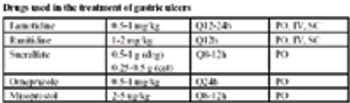
The stomach plays a key initial role in digestion through its mixing actions, and through the secretion of gastric acid and pepsin, which are important for the activation of key digestive enzymes.
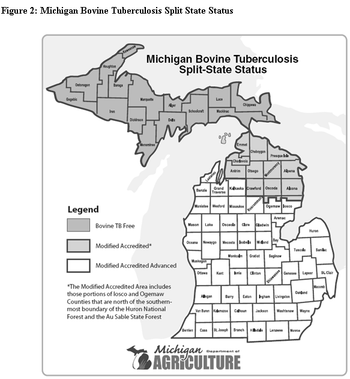
Bovine Tuberculosis (bTB) is an infectious bacterial disease that poses a risk to domestic livestock and wildlife in the United States (U.S).

Diagnosis of viral infections is an important component of small animal patient care.

The testicles in the stud dog are housed in the scrotum, a skin sac located between the thighs.

The genetic diversity that occurs among isolates of BVDV is characteristic of RNA viruses that exist in nature as quasispecies (a swarm of viral mutants).

Complete herd health programs should be a mainstay of production animal practice; however, I find these programs are rarely revisited by the veterinarian and the producer resulting in "antigenic shift" towards unrealistic programs for which the veterinarian is still considered the source.