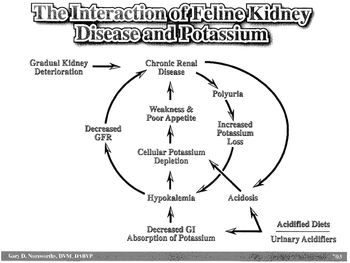
I much prefer creatinine over BUN.

I much prefer creatinine over BUN.

The fluids most frequently sampled for cytology are peritoneal, pleural, synovial, cerebrospinal and pericardial fluids and washes of the respiratory tract. Some of these fluids are more easily obtained than others. All may potentially yield general, or sometimes more specific information about a disease process.

Antimicrobial drugs are the most frequently prescribed drugs in veterinary medicine. They are also frequently used incorrectly, which can lead to treatment failure and the development of resistant bacteria.
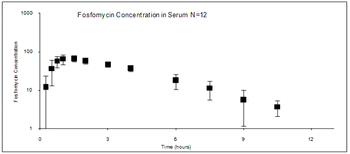
Treatment of urinary tract infections offer an example of the hazards and difficulties encountered when initial response is insufficient. Treatment of bacterial UTI offers a good example of how treatment of bacterial infections might be approaches. The goal of drug therapy has been to eliminate bactiuria, but this goal should be modified to include eradication of infection while minimizing the advent of resistance.

Inflammatory lesions may present as visible or palpable lumps, bumps, plaques, ulcers, accumulations of excessive fluid, or as abnormalities in organs that are visualized using imaging techniques. Cytologic examination of these types of lesions may be definitively diagnostic in many cases, or contribute to a diagnosis in other cases. When certain types of infectious agents are present, cytologic examination may be particularly rewarding.

Clinically significant drug interactions are rarely reported in veterinary medicine, however the incidence is probably far greater than is reported. With the introduction of more and more veterinary drugs, as well as the use of more human drugs in animals, the incidence is likely to increase in the next few years.
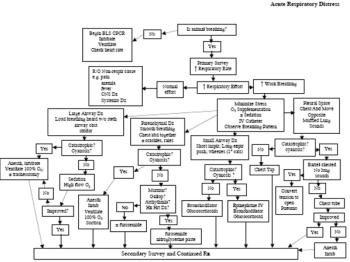
Acute respiratory distress (ARD) is the sudden onset of rapid and/or labored respiratory. It can be caused by pathology or obstruction associated with the nasal passages, oral cavity, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, alveoli, pulmonary vasculature or lymphatics, pulmonary innervation, chest wall, diaphragm, or pleural space.

Successful, efficient, sterile placement of intravenous (IV) catheters should be mastered by all providing care of the emergent patient. It should be understood that placement of short, large-bore peripheral catheters provide the most rapid means for intravascular volume expansion.
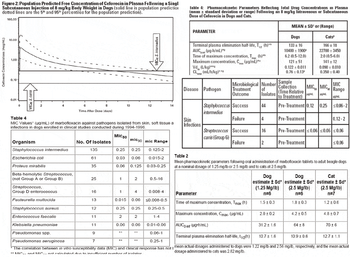
Today's drug package insert (DPI) can be a powerful ally in the selection and judicious use of a drug. The information that it provides might be categorized as either Product Description, Product Efficacy or Product Safety with some overlap among the categories. The order presented here may not be followed on the package insert. Paramount to understanding the use of a DPI is understanding what constitutes a PI.
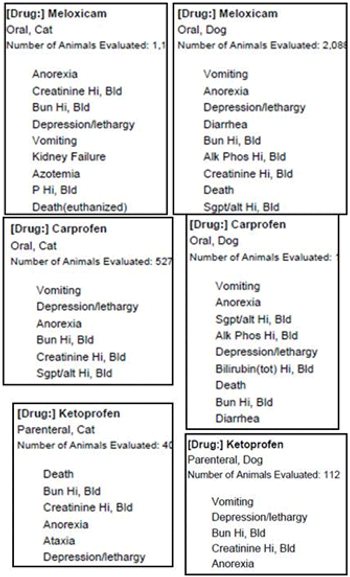
The cat as a species represents a therapeutic challenge when trying to use NSAIDs safey, including the newer drugs. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs block the first step of prostaglandin synthesis by binding to and inhibiting cyclooxygenase This action is both dose and drug dependent.
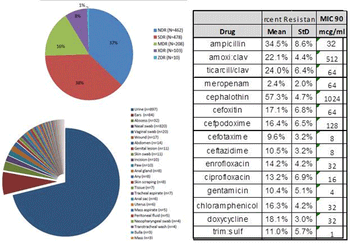
The advent of antimicrobial resistance is increasingly limiting therapeutic options in human and veterinary medicine. The ability of organisms to develop resistance to an antimicrobial varies with the species and strain.

Disturbances of acid-base equilibrium occur in a wide variety of critical illnesses and are among the most commonly encountered disorders in the intensive care unit (ICU). In addition to reflecting the seriousness of the underlying disease, disturbances in hydrogen ion concentration ([H+]) have important physiologic effects.
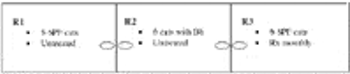
The 2 major differentials for elevated body temperature (> 102.5 F) are fever (pyrexia) and hyperthermia. Hyperthermia results from increased muscle activity, increased environmental temperature, or increased metabolic rate (i.e. hyperthyroidism). Fever develops when the thermoregulatory set point in the hypothalamus is increased, resulting in increased body temperature from physiologic mechanisms inducing endogenous heat production or heat conservation.

Vomiting is one of the most common medical presentations to the emergency room. It is not uncommon for the dog or cat to eat grass or their food and vomit – and subsequently go about their lives unaffected. So – when is vomiting an emergency? While there are no simple, nor clear cut answers, the simple guidelines in the box can guide the triage nurse or doctor.

Cytology is a relatively easy, relatively non-invasive, fast and inexpensive diagnostic technique. Sometimes you actually get the diagnosis. Other times you don't get a specific diagnosis, but the cytologic findings can help you decide which diagnostic technique might be indicated as a next step. Also some potential diagnoses often can be ruled out.

The term adverse drug reaction includes any undesired effect of a drug, including a lack of the desired effect. Adverse reactions to veterinary drugs can range from minor to severe and life-threatening.

The success of any fixed dosing regimen most often is based on the patient's clinical response to the drug. Fixed dosing regimens are designed to generate plasma drug concentrations (PDC) within a therapeutic range, ie, achieve the desired effect while avoiding toxicity.
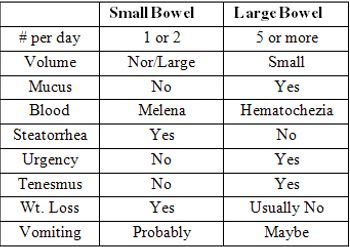
Most chronic vomiting and chronic diarrhea in cats originate in the small bowel.

The veterinary practitioner may be involved in some cases where pain management with NSAIDs or opioids is not possible due to the unacceptable risk of adverse effects.

Abdominal hemorrhage can result from disruption of a "blood" organ such as the liver or spleen, damage or avulsion of an abdominal artery or vein, or coagulation defect. The presence of blood in the abdomen can result in acute and severe pain from the abdominal cavity, abdominal organs or the nerves, muscles, fascia or skin associated with the abdomen.

Lumps and bumps that are cutaneous or subcutaneous often lend themselves very well to cytologic evaluation. They are easy to get to and most animals don't require sedation or anesthesia for you to obtain these samples. Although a definitively diagnostic sample isn't always obtained, the investment of time and equipment is minimal, and may give you the answer quickly and inexpensively.

Many of the reproductive abnormalities that present as emergencies are straight-forward and relatively easy to resolve. Treatment of these diseases, however, requires knowledge of the underlying pathophysiology as well as the options available for dealing with such emergencies.

Individualized drug therapy increasingly is being recognized as an important aspect of health care for both human and veterinary medicine. Consequently, veterinarians must reach beyond FDA-approved veterinary products to provide the current standard of veterinary care to their patients.



Help figure out what's causing this dog's weight loss despite a healthy appetite in this interactive case.




What's causing this cat's respiratory problems?