
With the increase in concurrent use in small animal patients, drug interactions are becoming more and more likely. Polypharmacy can have a number of unintended side effects.

With the increase in concurrent use in small animal patients, drug interactions are becoming more and more likely. Polypharmacy can have a number of unintended side effects.

Commonly affecting the large breed deep chested breeds gastric dilatation and volvulus syndrome has the potential to be a life threatening problem.

The neonatal period is defined as from birth to 2-4 weeks of age for puppies and kittens, with the pediatric period defined as up to 12 weeks of age. Because of major changes in physiology during this period, drug disposition and response are likely to be varied.

The manual PCV and plasma protein are quick, reliable methods for determining blood volume and hydration status when performed correctly. However, more than a bare-bones level of hematologic information has been made available with advances in technology.

Hypovolemia vs. dehydration

The title of this presentation is apropos, considering the fact that there are over 9,000 species of birds and nearly 8,000 species of reptiles. Knowing how different the hematology is between dogs and cats exemplifies how different eagle hematology may be from a parrot, or an iguana from a snake.
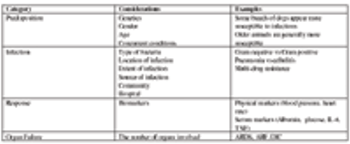
Sepsis is defined as the systemic inflammatory response to an infection. We commonly see patients that have a clinical presentation that appears similar to sepsis, but no source of infection can be identified. This syndrome has been termed the systemic inflammatory response syndrome or SIRS.

QA, as it relates to the clinical laboratory, is an all encompassing program for the systematic monitoring and evaluation of the various aspects of producing laboratory results to ensure that standards of quality are being met.

When a patient first arrives we have all been taught the ABCs of emergency care. We know that the assurance of a clear airway is paramount and the first thing we should all do, and then we move one to B and assure breathing is adequate. Then we move on to C (for cardiovascular) and assess and ensure the heart is pumping and pumping adequately... This process is termed vertical resuscitation and is a "step by step" process that is completed in a "priority of need" sequence.

The principles of management of patients with severe lung disease and injury are summarized and the cases depicting the use if these management techniques are presented

This session will discuss basic methodologies used by selected common biochemistry analyzers and quality assurance issues which may result in better understanding of the advantages and disadvantages of various instrument types and ultimately assist with instrument selection.

From the very first time I was faced with the responsibility of possibly having to respond to an emergency when I was a young boy scout (at age 11) to just yesterday when I was an emergency clinician at the Pet Emergency Clinic, the immediate goal was "to make everything ready".

Practical management of severe wounds and open fractures begins with initial assessment and management. The first priority is the control of severe hemorrhage that may be associated with the injury.

The first step in empirical antimicrobial therapy is to first critically ask whether there is good evidence of a bacterial infection. Too often, antimicrobials are prescribed on a 'just in case' basis or because an owner resists additional diagnostics.

zoonosis hookworms

zoonosis toxoplasmosis

The Five looks at changing trends in veterinary medicine, a policy change at a major university, and efficiency tips for practice managers.

Davis, Calif. -- The new North American Veterinary Regenerative Medicine Association wants to recruit medicine researchers, stem cell biologists, and others with an interest in stem cell therapy.

ClinQuiz: Tick particulars, answer 2A

ClinQuiz: Tick particulars, answer 2A

ClinQuiz: Tick particulars, answer 1B

ClinQuiz: Tick particulars, answer 3B

ClinQuiz: Tick particulars, answer 2B

ClinQuiz: Tick particulars, answer 3A

ClinQuiz: Tick particulars, answer 2C

ClinQuiz: Tick particulars, answer 3C

ClinQuiz: Tick particulars, answer 1C

Remember Pet Rocks? They might have been a short-lived fad, but I think they're still alive and well in the U.S.
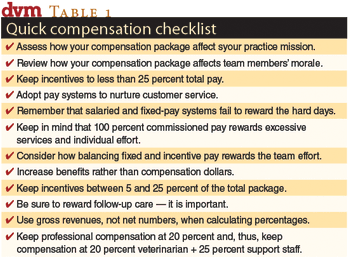
Happy associates deliver great customer service. Pay them right.

It's a whole new set of challenges.