
In this Q&A, Marty Becker, DVM, Elite FFCP-V and Paul Bloom, DVM, DACVD, DABVP (Canine and Feline), Elite FFCP-III share extensive advice on how to minimize fear, anxiety, and stress in patients

In this Q&A, Marty Becker, DVM, Elite FFCP-V and Paul Bloom, DVM, DACVD, DABVP (Canine and Feline), Elite FFCP-III share extensive advice on how to minimize fear, anxiety, and stress in patients

A boarded dermatologist shares his expertise in handling this inflammatory condition

Dr. Paul Bloom delivers a quick perspective on steroids and antihistamines versus newer products for your allergic canine veterinary patients.

To get to the bottom of a tough otitis presentation in a patient, it's time for technicians to perform a little sleuthing.

Veterinary technicians: You can help patients with dermatology issues

You just got new additions to your arsenal against atopy, demodicosis and bacterial skin infections.

Five pointers on managing this common autoimmune dermatologic disease from veterinary dermatologist Dr. Paul Bloom.

Top mistakes veterinarians make in dermatology work ups.

Dr. Paul Bloom gives his dosing protocol for long-term cyclosporine therapy in dogs.
Pick the right diagnostic step in this senior dog.

Dr. Paul Bloom discusses the importance of setting realistic client expectations.

Suggestions for managing a case of superficial folliculitis in dogs.
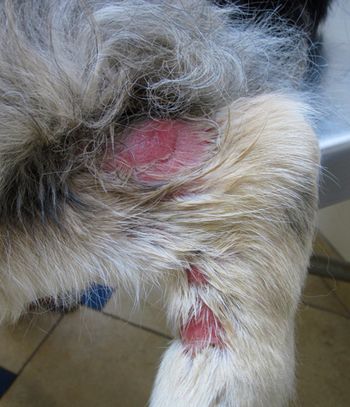
Can you determine the best treatment for this dog?

The diagnosis of ANY skin disease is based on detailed history taking, clinical findings (identification of primary lesions, distribution of lesions), laboratory testing and therapeutic trials. For autoimmune skin diseases (AISD) the most beneficial laboratory procedure is histopathologic evaluation.

It is important to understand that ear disease is only a symptom (no more specific than pruritus). As Dr Flemming Kristensen stated A patient showing ear problems is a dermatology case until proven otherwise. It is appropriate therefore to approach the diagnosis of ear disease just as you would for any other skin disease.

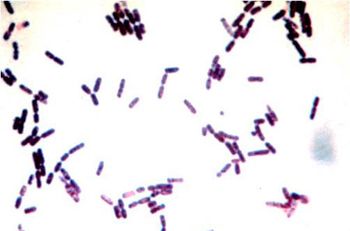
Bacterial pyoderma is more common in the dog than any other mammalian species. Currently Staphylococcus virulence factors such as protein A, leukocidin, hemolysins, epidermolytic toxin have not been shown to be to play a role in canine pyoderma as opposed to humans with Staphylococcus aureus infections.

Malassezia is a genus of lipophilic yeast found as a commensal of the skin and mucosal surfaces that may cause skin disease in a variety of mammalian species.

Bacterial pyoderma is more common in the dog than any other mammalian species. Currently Staphylococcus virulence factors such as protein A, leukocidin, hemolysins, epidermolytic toxin have not been shown to be to play a role in canine pyoderma as opposed to humans with Staphylococcus aureus infections.

Vasculitis is characterized by an aberrant immune response directed toward blood vessels. Histologically there is an inflammatory response involving and destroying blood vessels leading to ischemic changes (see histopathology). A vasculopathy is a disease process in which tissue changes are consistent with ischemia but histologically vasculitis can't be identified.

Itraconazole (Sporonax ?-Janssen Pharmaceuticals- 100 capsules and 10 mg/ml oral solution)) is a member of the azole family of antifungal agents. Imidazoles (Imidazole family (thiabendazole, clotrimazole, ketaconazole, miconazole and enilconazole) and triazoles (itraconazole and fluconazole) make up this family of drugs.
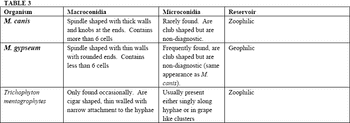
Protocols are useful in helping to diagnose and treated many different disorders. Part of any good protocol should be a minimum data base (MDB). In addition to signalment, history, etc in veterinary dermatology laboratory testing should be a component of this data base.

It is important to understand that ear disease is only a symptom (no more specific than "pruritus"). As Dr Flemming Kristensen stated "A patient showing ear problems is a dermatology case until proven otherwise". It is appropriate therefore to approach the diagnosis of ear disease just as you would for any other skin disease.

Malassezia is a genus of lipophilic yeast found as a commensal of the skin and mucosal surfaces that may cause skin disease in a variety of mammalian species. In normal dogs these organisms are present in very small numbers on the skin (fold areas-lip, vulvar, axillae, interdigital), oral and anal mucosal surfaces, in the ear canals and anal sacs. In contrast to Candida, MD is not associated w/recent antibiotic administration, in fact, there appears to be a symbiotic relationship between the surface staphylococcal organisms and the yeast.

The diagnosis of ANY skin disease is based on detailed history taking, clinical findings (identification of primary lesions, distribution of lesions), laboratory testing and therapeutic trials. For autoimmune skin diseases (AISD) the most beneficial laboratory procedure is histopathologic evaluation.

Alopecia in the dog is a common clinical finding. It is most commonly associated with pruritus due to allergic skin disease. There are also many causes of nonpruritic alopecia. Since the skin and hair can only "react" in a limited manner regardless of the triggering event, signalment, history (hx), physical exam (PE) and laboratory testing (eg skin scrapings, skin biopsies, fungal cultures, endocrine testing, intradermal testing, etc) all may be needed to help determine the underlying cause.

Dr. Paul Bloom suggests options for this Great Dane.

Veterinary dermatologist Dr. Paul Bloom discusses how he handles these cases.

Dr. Paul Bloom reviews the recommended protocol for successful bacterial culture of skin and, in particular, skin biopsies.

Veterinary dermatologist Dr. Paul Bloom gives his thoughts on this reader question.

Dermatologic disease is one of the most common reasons owners bring their dogs to the veterinarian.

Published: December 1st 2012 | Updated:

Published: December 4th 2012 | Updated:

Published: December 1st 2010 | Updated:

Published: December 1st 2010 | Updated:

Published: December 1st 2009 | Updated:

Published: April 1st 2009 | Updated: