
W. F. Young introduces a 30-day supply of Hooflex Plus, pelleted hoof supplement in a resealable bag.

W. F. Young introduces a 30-day supply of Hooflex Plus, pelleted hoof supplement in a resealable bag.

FlavorTek introduces Flavor-Doh to help administer pills in dogs.

In my experience, metaldehyde toxicosis is one of the most common toxicoses in dogs.

Wedgewood Pharmacy introduces Pimobendan capsules.

For cats with Elizabethan collars, eating or drinking from a bowl on the floor can be difficult.

Schaumburg, Ill. - The American Veterinary Medical Association wants no part of any signed pact with the Human Society of the United States - even when endorsing mutually supported initiatives.

Here's a quick sample of the type of compliments you can offer to bring a smile to your team members' faces

The Snowycycle cart was created to help rehabilitate pets by preventing atrophying while building and restoring muscle mass.

Harrisburg, Pa.- Pennsylvania lawmakers are considering tough legislation mandating drug-risk disclosure and prescreening animals prior to pharmaceutical use if recommended by a drug maker.

RMCards.com introduces direct mailing full-color reminders to clients from veterinary offices.

Novartis introduces a Web site designed to help owners identify and seek treatment for skin problems in their dogs.

EPS Inc. announces the addition of six sizes of disposable beakers to its growing line of compounding and dispensing accessories.
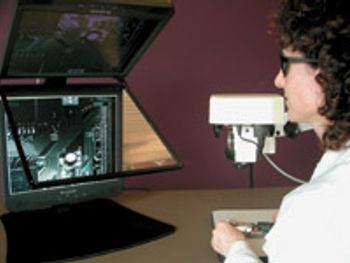
Micro Vision Systems (MVSI) introduces TrueVision®, a real-time, high-definition, 3-D image-capture and display system for stereomicroscopes.

In the May issue, I briefly told my mother's life story and related that my grandparents were immigrants. There is more to this story.

EPS introduces Autosqueeze, a device that helps patients with weak or arthritic fingers easily grasp and dispense ophthalmic medication.

Fort Dodge Animal Health announces the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved the use of Flunixamine? (flunixin meglumine injection) in lactating dairy cows.
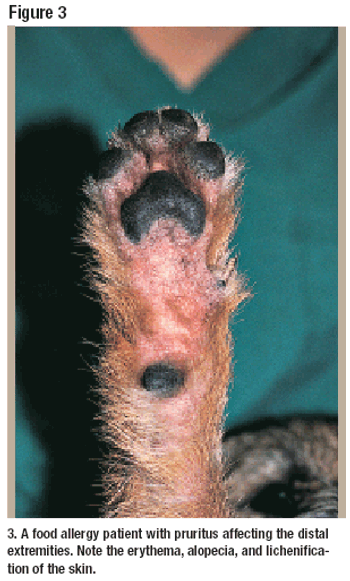
Corticosteroids are among the most used and misused medications in veterinary medicine. They exert a powerful, reliable, and rapid effect, and there is no viable, more effective therapeutic alternative in animals with certain skin conditions. Topical and oral corticosteroid therapies are considered the first choice for treatment of acute and chronic inflammatory skin diseases, particularly allergic dermatitis. In addition, they aid in the inflammation associated with some types of infections, primarily Malassezia dermatitis and otitis.

Cats are sensitive to many toxic agents, sometimes in ways unique to their species.

Unotron introduces SpillSeal® washable computer keyboard and mouse combination.

I don't know who Maeterlinct was, but I'll bet he would not expect the Association of American Veterinary Medical Colleges (AAVMC) to find anything they did not like in their study to forecast veterinary medicine's future, which is reported as envisioning the future in academic veterinary medicine.

Securos announces the release of its new line of casting and splinting products OrthoCast and OrthoSplint.

Raleigh, N.C. - Officials at North Carolina State University hope a newly dedicated research center will lead to medical advances in animal and human medicine.

Bayer announced the release of its new Drontal Plus Taste Tabs (praziquantel/pyrantel pamoate/febantel), a deworming treatment for dogs.

Marketing Tip June 06
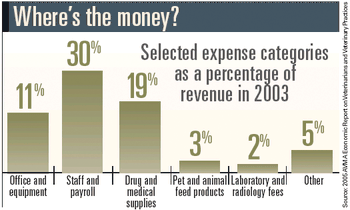
National Report - Dr. Al Schwartz likens general practice to a dying breed, consumed by a growing number graduates electing tracks in specialty medicine.

Do you read Firstline cover-to-cover? Have you successfully implemented a tip you found in Pearls of Practice? Tell us how you use Firstline.

CEA

Jorgensen introduces the padded equine recovery hood for anesthesia recovery.

Instead of having owners administer eardrops into their dogs' ears directly from the bottle and count the drops as they go, we give them a tuberculin syringe to use.

We pierce holes in the lids of the rubbing alcohol and hydrogen peroxide containers with a 16-ga needle, allowing us to squirt the fluid straight from the bottle to wherever we need it.